
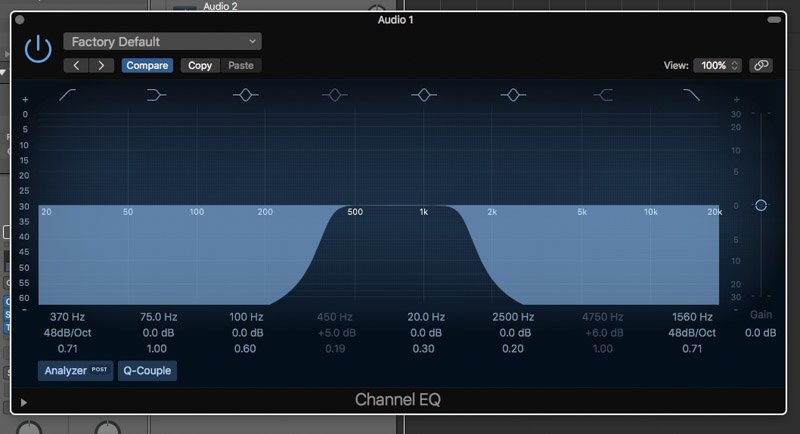
There are some we can hear better than others. Recall that men have deeper voices while women have sharper ones different pitch and frequencies. There is a whole range of frequencies that the human ear simply can’t detect and a dog whistle is a great example of just one such frequency. Different music instruments and even the human voice spans across different frequencies. Like light exits on many different wavelengths, sound exists across many different channels or frequencies. The frequencies it supports are from 100Hz – 10kHz.Īn equalizer lets you adjust the frequency of different sound channels. They’ve been around for a long time, since the age of cassette players and here’s a picture of what the equalizer on my cassette player from 1000 B.C. We’re going to take a look at what the equalizer is and just what each of those sliders mean.Įqualizer settings aren’t an invention of the digital music era. But what are these mystery settings that claim to improve our listening experience? Are they even real or is it just something developers the world over have collectively conspired to add to music players for the sake of looking cool? The equalizer settings are 100% legit as is the claim that the right setting will improve the quality of music you hear, subject to what kind of speakers you have. These pre-sets are defined by the genre they’re best suited for such as pop or rock (but never with a goth metal satanic screaming pre-set for some reason). For example, high quality bells have an approximately pure sinusoidal tone for a long time after being struck by a hammer.The best music players have music equalizer settings and come with pre-sets to make the music you’re listening to sound really good. A higher quality factor implies a lower attenuation, and so high Q systems oscillate for long times. That is, the attenuation parameter \alpha represents the rate of exponential decay of the oscillations (e.g., after an impulse) of the system. Equivalently, it compares the frequency at which a system oscillates to the rate at which it dissipates its energy.Įquivalently (for large values of Q), the Q factor is approximately the number of oscillations required for a freely oscillating system's energy to fall off to 1/e^ \,įor this system, when Q > 0.5 (i.e., when the system is underdamped), it has two complex conjugate poles that each have a real part of \alpha. It is a dimensionless parameter that compares the time constant for decay of an oscillating physical system's amplitude to its oscillation period. Physically Speaking, Q is 2\pi times the ratio of the total energy stored divided by the energy lost in a single cycle or equivalently the ratio of the stored energy to the energy dissipated over one radian of the oscillation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
